Barrett's Esophagus Specialists: Experts in Diagnosing and Managing a Silent Condition
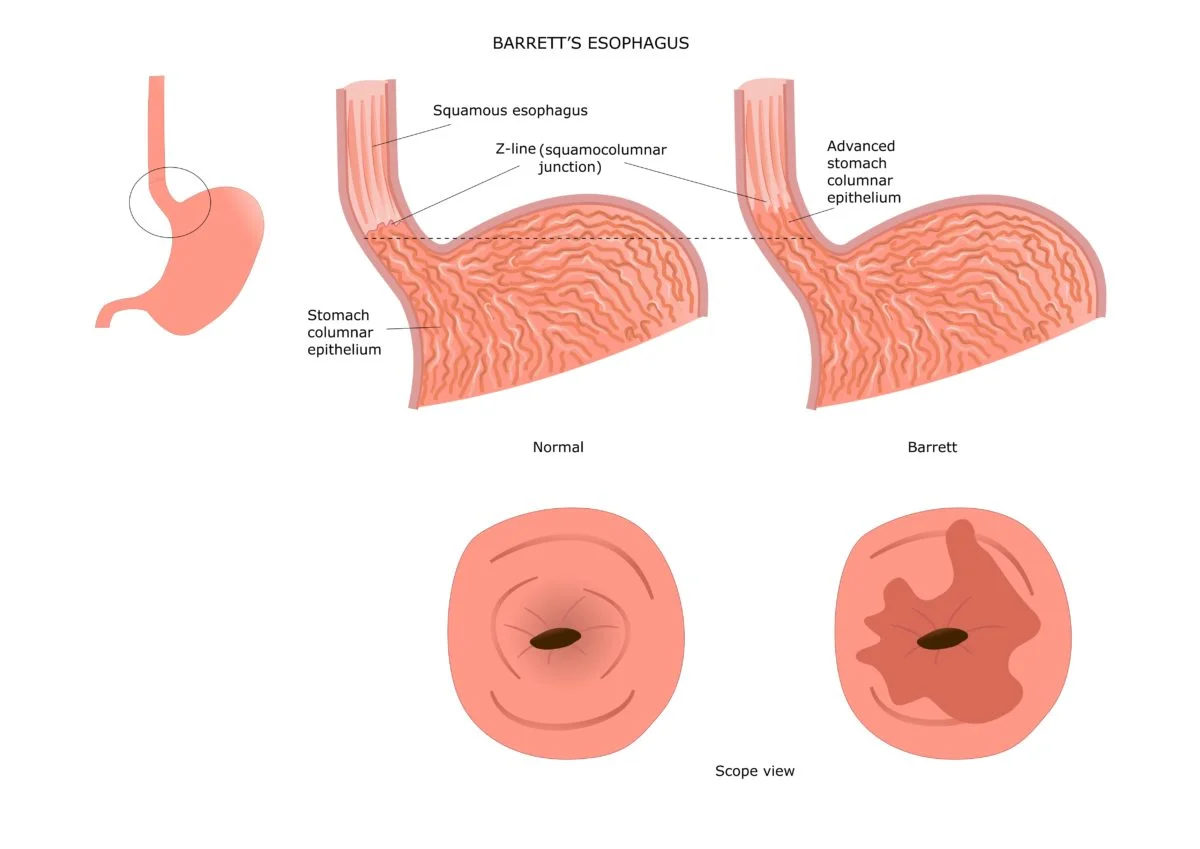
Barrett's Esophagus is a condition that often develops silently but can lead to serious complications if left untreated, including a significantly increased risk of esophageal cancer. With its subtle symptoms and long-term risks, early diagnosis and proper management by experienced specialists are crucial. Barrett’s Esophagus specialists are gastroenterologists or surgical experts who focus on identifying, monitoring, and treating this potentially dangerous condition with precision and care.
What Is Barrett’s Esophagus?
Barrett's Esophagus is a condition where the normal squamous cells lining the esophagus are replaced with columnar cells, which are more similar to the cells found in the intestine. This change—known as intestinal metaplasia—is usually a response to chronic acid exposure from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
While Barrett’s Esophagus itself isn’t cancer, it significantly increases the risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma, a serious and potentially deadly form of cancer. Therefore, patients diagnosed with this condition often require lifelong monitoring and, in some cases, therapeutic intervention.
The Role of Barrett’s Esophagus Specialists
Managing Barrett’s Esophagus is not just about treating symptoms—it involves a comprehensive strategy for early detection, surveillance, risk assessment, and treatment. This is where specialists come in.
1. Accurate Diagnosis
Specialists use advanced diagnostic tools such as:
- Upper endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to look for changes in tissue color and structure.
- Biopsy: During endoscopy, small samples of esophageal tissue are taken for histological analysis.
- Esophageal pH monitoring: This assesses the level of acid exposure in the esophagus to determine the severity of GERD.
2. Dysplasia Grading and Surveillance
Barrett's Esophagus can be classified as:
- Non-dysplastic Barrett’s: No signs of precancerous changes.
- Low-grade dysplasia (LGD): Minor changes indicating early signs of precancerous activity.
- High-grade dysplasia (HGD): Significant changes with a higher likelihood of developing into cancer.
Specialists follow strict surveillance guidelines depending on the severity of the dysplasia. Regular endoscopies are typically recommended every 3–5 years for non-dysplastic Barrett’s, while patients with dysplasia may require more frequent monitoring or immediate treatment.
3. Treatment Options
Barrett’s Esophagus treatment varies based on the risk level:
- Medication: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are used to reduce acid reflux, helping to prevent further damage.
- Endoscopic therapy: This includes procedures like:
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA): Burns away abnormal cells using heat.
- Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR): Removes abnormal tissue for both diagnosis and treatment.
- Cryotherapy: Freezes and destroys dysplastic cells.
- Surgery: In rare cases, esophagectomy (removal of part of the esophagus) may be necessary, especially in early-stage cancer.
Barrett’s Esophagus specialists are trained in these techniques and will recommend the most effective treatment based on individual patient profiles.
Why Choosing a Specialist Matters
Barrett’s Esophagus is a nuanced condition that requires careful attention to detail. General physicians may treat GERD effectively, but when it comes to Barrett’s, the expertise of a specialist can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Key Benefits of Seeing a Specialist:
- Early Detection of Precancerous Changes: Specialists are trained to detect even subtle signs of dysplasia.
- Advanced Endoscopic Skills: They are equipped with cutting-edge tools and minimally invasive techniques.
- Personalized Monitoring Plans: Ongoing care is tailored to the patient’s level of risk.
- Collaborative Care: Specialists often work within multidisciplinary teams, including pathologists and oncologists, to ensure comprehensive care.
How to Find a Barrett’s Esophagus Specialist
Finding the right specialist is essential for long-term management. Here are some tips:
- Look for board-certified gastroenterologists with experience in Barrett’s Esophagus.
- Choose a center with a strong reputation in gastrointestinal health, such as an academic medical center or dedicated digestive disease clinic.
- Ask about advanced treatment options, including RFA, EMR, and cryotherapy.
- Read patient reviews and ask for referrals from primary care doctors or general gastroenterologists.
Living with Barrett’s Esophagus: Patient Outlook
With proper management, many people with Barrett’s Esophagus live healthy, full lives. Lifestyle modifications—such as weight loss, smoking cessation, dietary changes, and elevating the head during sleep—can help reduce GERD symptoms and prevent further esophageal damage.
More importantly, consistent follow-up with a specialist helps monitor for dysplasia or early signs of cancer, allowing for timely intervention and vastly improved outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Barrett’s Esophagus may begin as a silent condition, but its implications are serious. Specialists in this field bring a deep understanding of the disease, access to life-saving technologies, and a patient-centered approach to care. Whether you're newly diagnosed or seeking a second opinion, consulting a Barrett’s Esophagus specialist is a crucial step toward safeguarding your long-term health.










