Risks and side effects of chemical peels in Riyadh
Risks and side effects of chemical peels in Riyadh
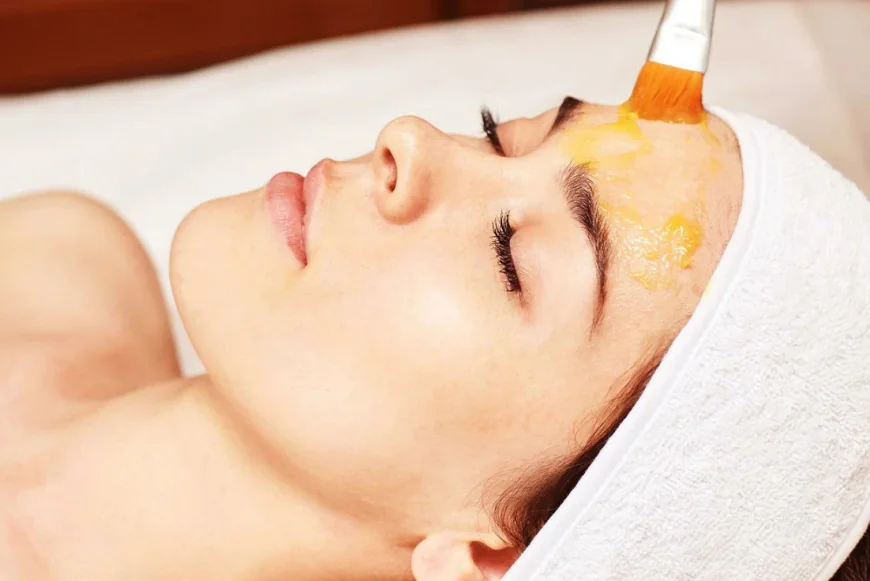
Chemical peels are a popular and effective cosmetic procedure widely used in Riyadh for improving skin texture, tone, and overall appearance. They work by applying a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the outer layers, stimulates cell turnover, and encourages collagen production. While chemical peels offer numerous benefits, it is essential to understand that, like any cosmetic procedure, they carry potential risks and side effects. Being aware of these factors helps individuals make informed decisions, minimize complications, and ensure optimal outcomes. Chemical peels in Riyadh offer an effective solution for rejuvenating the skin, reducing pigmentation, and achieving a brighter, smoother complexion.
The risks associated with chemical peels largely depend on the type of peel used, the skin type, the skill of the practitioner, and pre-existing skin conditions. Superficial peels, which use mild acids like glycolic or lactic acid, generally have fewer risks and minimal downtime. Medium and deep peels, which penetrate more layers of the skin to address more pronounced issues, carry a higher likelihood of side effects and require more careful aftercare. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals in Riyadh, where environmental factors such as sun exposure, dust, and dry air can influence skin sensitivity and recovery.
One of the most common side effects of chemical peels is redness and irritation. After the procedure, it is normal for the skin to appear flushed and feel slightly sensitive, similar to a mild sunburn. This effect is usually temporary and subsides within a few hours to several days, depending on the peel’s depth. Superficial peels may cause minimal redness, while medium and deep peels often result in more pronounced irritation that requires careful post-peel care, including gentle cleansing, hydration, and sun protection.
Peeling and flaking are also expected after chemical peels, as the skin sheds the damaged outer layers to reveal fresher skin underneath. While this process is part of the treatment’s effectiveness, excessive or uneven peeling can sometimes occur, especially if post-treatment care is not followed properly. In Riyadh, where dry air can exacerbate skin dehydration, moisturizing regularly with non-comedogenic creams and avoiding harsh skincare products is essential to minimize discomfort and ensure uniform peeling.
Hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation are potential risks, particularly for individuals with darker skin tones or those prone to pigmentation changes. Hyperpigmentation occurs when certain areas of the skin darken after the peel, while hypopigmentation refers to lightened patches. Both conditions can result from improper peel application, excessive sun exposure, or underlying skin sensitivity. In Riyadh, where sun exposure is intense, diligent use of broad-spectrum sunscreen before and after the procedure is crucial to prevent pigmentation issues and protect the healing skin.
Scarring is a less common but more serious risk of chemical peels. It is more likely to occur with medium or deep peels, particularly if the skin is prone to keloids or if the peel is performed incorrectly. Following the practitioner’s instructions for aftercare and avoiding scratching, picking, or applying harsh products on the treated skin significantly reduces the risk of scarring.
Infection is another potential side effect, although it is relatively rare when proper hygiene and professional techniques are used. The chemical solution temporarily disrupts the skin barrier, which can make it more vulnerable to bacteria or viruses. Cold sores or herpes outbreaks may also be triggered in individuals with a history of such conditions. Pre-treatment screening and preventive antiviral medication, if recommended, can minimize the risk of infections in Riyadh’s climate, where dust and environmental pollutants may increase the likelihood of skin irritation.
Allergic reactions to the chemical solutions used in peels can occur, though they are uncommon. Symptoms may include itching, swelling, or rashes. A patch test or professional assessment before the procedure helps identify potential sensitivities and prevent severe allergic responses.
Finally, uneven results can be considered a minor but notable concern. If the peel is not applied uniformly or if post-care is inconsistent, the skin may appear blotchy, uneven, or mottled. Proper technique, careful selection of peel type, and adherence to aftercare instructions are essential to achieving smooth, consistent results.
Mitigating risks and side effects involves professional evaluation, proper skin preparation, and careful aftercare. Individuals in Riyadh should seek treatment from qualified skincare professionals who can assess their skin type, recommend the appropriate peel, and provide clear guidance on pre- and post-treatment care. Avoiding sun exposure, using gentle skincare products, keeping the skin hydrated, and following all professional instructions significantly reduce the likelihood of complications.
In conclusion, while chemical peels offer significant benefits for skin rejuvenation, acne scars, pigmentation, and overall radiance, they are not without risks and side effects. Common issues such as redness, peeling, and irritation are generally temporary, while hyperpigmentation, scarring, infection, and allergic reactions are less frequent but require careful attention. In Riyadh, where environmental factors can influence skin sensitivity, choosing the right peel, seeking professional guidance, and adhering to post-peel care are essential to ensure safety and achieve optimal results. Understanding and preparing for these potential risks allows individuals to enjoy the transformative benefits of chemical peels while minimizing complications.










