Introduction to Stem Cell Therapy: Types and Uses
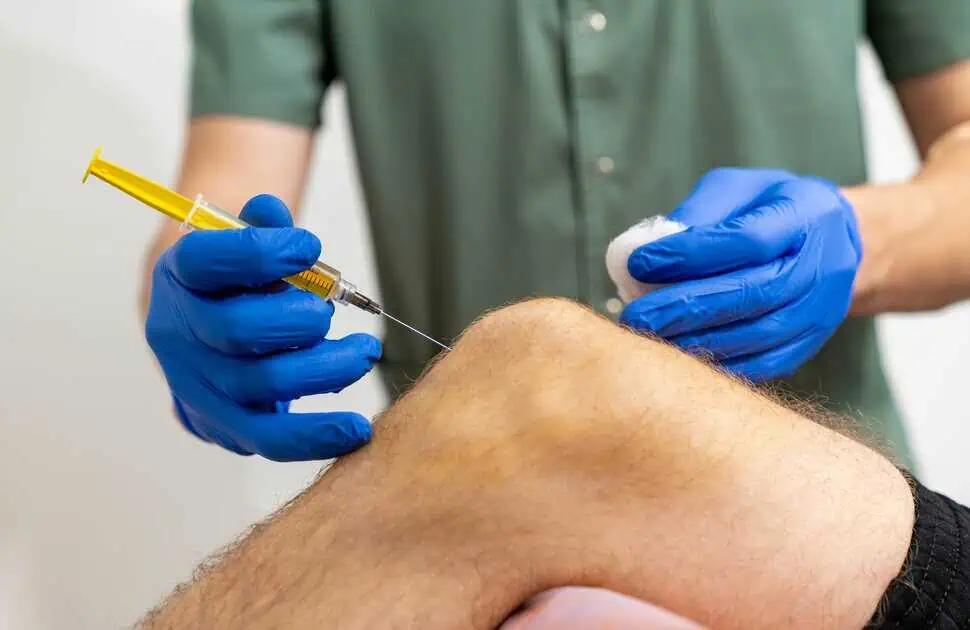
Stem cell therapy is an innovative field in medical science that explores the unique abilities of stem cells to repair, replace, and regenerate damaged tissues. These therapies harness the natural potential of stem cells to transform into specialized cells, providing hope for various medical conditions. Understanding the types of stem cells and their applications is essential for appreciating the impact of this cutting-edge treatment.
Understanding Stem Cells
Stem Cell Therapy Dubai are undifferentiated cells with the ability to develop into different cell types in the body. They play a crucial role in growth, repair, and maintaining the body's natural balance. Their unique properties include self-renewal, where they can divide and create more stem cells, and differentiation, where they can become specialized cells such as nerve, muscle, or blood cells. Stem cell therapy utilizes these capabilities to treat a wide range of medical issues.
Types of Stem Cells
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are derived from early-stage embryos and have the potential to develop into any cell type in the body. Their versatility makes them highly valuable in research and therapy development. They are studied for their ability to regenerate tissues and potentially treat conditions like spinal cord injuries and degenerative diseases.
Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells, also known as somatic stem cells, are found in various tissues, including bone marrow, blood, and the brain. These cells are more limited in the types of cells they can become compared to embryonic stem cells, but they are still crucial for maintaining and repairing tissue. Adult stem cells are commonly used in therapies for blood-related conditions and certain immune disorders.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPSCs, are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic-like state. This process allows them to regain the ability to differentiate into multiple cell types. iPSCs provide a promising approach to personalized medicine because they can be derived from a patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of immune rejection.
Perinatal Stem Cells
Perinatal stem cells are obtained from tissues associated with pregnancy, such as the umbilical cord, placenta, and amniotic fluid. These cells have properties between embryonic and adult stem cells, offering a balance of versatility and availability. They are increasingly explored for therapies involving tissue repair and immune system support.
Uses of Stem Cell Therapy
Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell therapy is a cornerstone of regenerative medicine, which aims to restore damaged tissues and organs. It has the potential to address conditions like heart disease, spinal cord injuries, and neurodegenerative disorders. By replacing damaged cells, stem cell therapy can enhance healing and improve overall function.
Blood and Immune System Disorders
Stem cells, particularly those from bone marrow, have been used extensively to treat blood-related disorders, including leukemia and lymphoma. They can regenerate healthy blood cells and support the immune system in fighting diseases. Bone marrow transplants are a well-known application of stem cell therapy for these conditions.
Orthopedic Conditions
Stem cell therapy is increasingly used in orthopedics to promote healing in bones, cartilage, and joints. This includes treatments for fractures, osteoarthritis, and tendon injuries. The therapy can stimulate tissue repair and potentially reduce the need for more invasive surgical interventions.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Research in stem cell therapy is expanding into the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. By generating new nerve cells, stem cells may help restore neurological function and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Cardiovascular Applications
Heart disease and vascular conditions can benefit from stem cell therapy through the regeneration of heart tissue and improvement of blood flow. Experimental treatments aim to repair damage caused by heart attacks or chronic conditions, offering new possibilities for cardiac care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do stem cells work in therapy?
Stem cells work by differentiating into the necessary cell type to repair or replace damaged tissue. They can also release signaling molecules that encourage the body’s own cells to regenerate and heal.

Are all stem cells the same?
No, stem cells vary based on their source and capabilities. Embryonic stem cells are highly versatile, adult stem cells are more specialized, and iPSCs are reprogrammed adult cells that regain versatility.
What conditions can stem cell therapy treat?
Stem cell therapy is being explored for a wide range of conditions, including blood disorders, orthopedic injuries, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular issues. Its applications continue to grow with ongoing research.
Is stem cell therapy personalized?
Some forms of stem cell therapy, such as those using iPSCs, are highly personalized because they use the patient’s own cells. This approach can reduce immune rejection and improve treatment outcomes.
How is stem cell therapy advancing medical research?
Stem cell therapy provides insights into disease mechanisms, drug testing, and tissue regeneration. It allows researchers to study how cells develop and respond to treatments, accelerating the discovery of new therapies.
Stem Cell Therapy in Dubai represents a significant advancement in medical science, offering new possibilities for healing and regeneration. Its types, ranging from embryonic to adult and induced pluripotent stem cells, each bring unique potential to medical applications. By exploring its uses, from regenerative medicine to treatment of complex disorders, it is clear that stem cell therapy is reshaping the future of healthcare.










