Hair Transplant vs Non‑Surgical Hair Loss Treatments
Learn how to prevent and treat hair transplant scars effectively. Discover modern techniques, aftercare tips, and solutions for natural-looking results for a Hair Transplant.
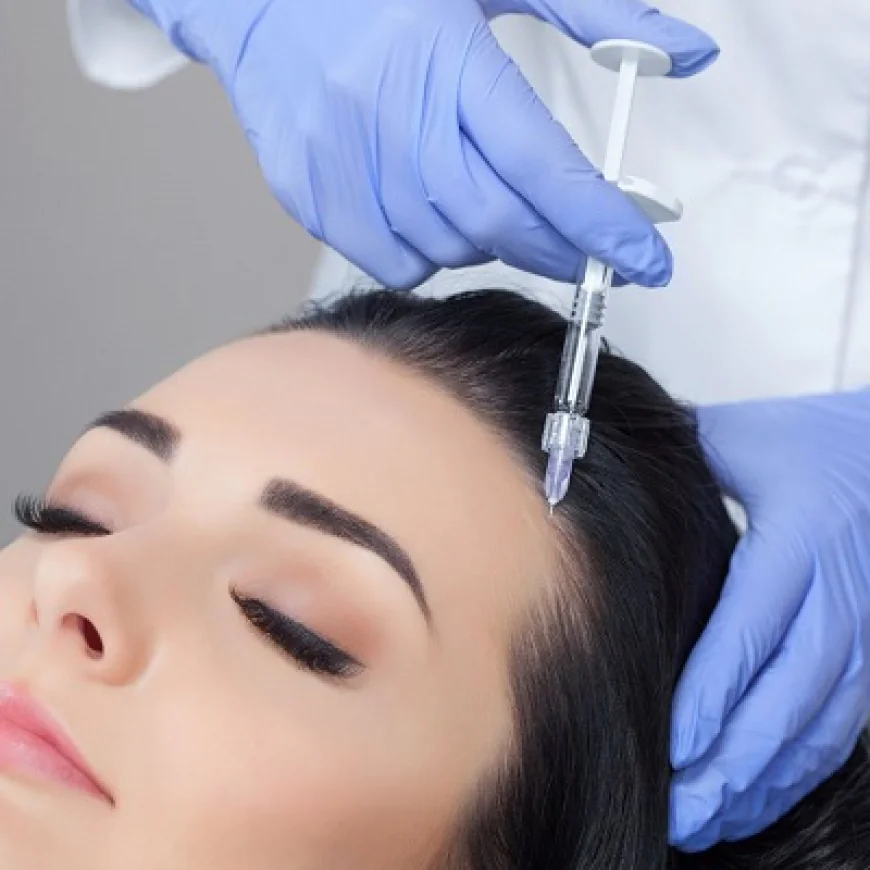
Hair loss is a common concern that affects both men and women, often impacting confidence and self-esteem. With numerous treatment options available today, deciding between a surgical Hair Transplant and non-surgical hair loss treatments can be challenging. Understanding the differences, benefits, and limitations of each approach is essential for making an informed decision. This article explores the comparison in detail, helping readers weigh the options effectively.
Understanding Hair Loss
Before comparing treatment options, it is important to understand the underlying causes of hair loss. Common factors include genetics, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, stress, medical conditions, and certain medications. The pattern and severity of hair loss often determine which treatment may be most effective. For instance, diffuse thinning may respond better to non-surgical methods, while localized bald spots may benefit more from hair transplantation.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from a donor area, usually the back or sides of the scalp, to areas affected by hair thinning or baldness. Two main techniques are commonly used:
-
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of scalp is removed from the donor area and dissected into individual follicular units for transplantation.
-
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area and implanted into the thinning regions.
Hair transplants offer a permanent solution by redistributing existing hair follicles, resulting in natural-looking density and hairline restoration.
Advantages of Hair Transplant
Hair transplants have several distinct advantages that make them appealing for long-term hair restoration:
-
Permanent Results: Transplanted hair follicles are typically resistant to the effects of hair loss, providing long-lasting coverage.
-
Natural Appearance: Modern techniques allow precise placement of follicles, resulting in a hairline that looks natural and blends seamlessly with existing hair.
-
Minimal Maintenance: Once the transplanted hair grows, it can be washed, cut, and styled like natural hair.
-
High Success Rate: Advances in surgical methods have improved graft survival and overall outcomes.
However, it is important to note that hair transplants require a sufficient donor area and involve a surgical procedure, which may include downtime for recovery.
Non‑Surgical Hair Loss Treatments
Non-surgical hair loss treatments offer alternatives for individuals who are not ready or suitable for surgery. These methods focus on stimulating existing follicles, slowing hair loss, or improving scalp health. Common non-surgical options include:
-
Topical Treatments: Minoxidil is a widely used topical solution that promotes hair growth and slows thinning.
-
Oral Medications: Finasteride and similar medications work by reducing the hormone responsible for hair loss.
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Laser devices stimulate blood flow and follicle activity to encourage hair growth.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Concentrated growth factors from a patient’s own blood are injected into the scalp to stimulate follicle regeneration.
-
Hair Thickening Products: Shampoos, conditioners, and serums designed to add volume or strengthen hair strands.
These treatments are generally non-invasive, easier to apply, and suitable for early stages of hair thinning.
Advantages of Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments offer several benefits:
-
Non-Invasive: No surgery or recovery time is required.
-
Flexible and Reversible: Treatments can be started, paused, or changed without permanent effects.
-
Early Intervention: Effective for slowing hair loss in its initial stages.
-
Convenience: Can often be applied at home, making them accessible and practical.
However, non-surgical methods typically require consistent use over time and may not produce dramatic results for advanced hair loss.
Comparing Hair Transplant and Non-Surgical Options
When choosing between a hair transplant and non-surgical treatments, several factors should be considered:
-
Severity of Hair Loss: Hair transplants are better suited for moderate to severe baldness or thinning, while non-surgical methods work well for early-stage hair loss.
-
Longevity of Results: Hair transplants offer permanent results, whereas non-surgical treatments require ongoing maintenance.
-
Cost and Commitment: Surgical procedures involve higher upfront costs and recovery time, while non-surgical treatments may have lower initial costs but require continuous use.
-
Desired Outcome: Those seeking significant restoration may benefit more from surgery, while individuals aiming to slow progression or enhance density may prefer non-surgical approaches.
Many patients find a combination of both approaches to be effective—for example, a hair transplant followed by ongoing non-surgical treatments to preserve native hair and optimize long-term results.
Post-Treatment Care
Regardless of the chosen method, proper post-treatment care is essential:
-
For Hair Transplants: Follow surgical instructions, maintain a clean scalp, avoid strenuous activities, and ensure proper nutrition to promote healing.
-
For Non-Surgical Treatments: Apply products consistently, protect hair from harsh environmental factors, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support hair growth.
Adherence to post-treatment guidance enhances the effectiveness and longevity of results.
FAQs
1. Can non-surgical treatments replace a hair transplant?
Non-surgical treatments are generally effective for slowing hair loss and improving density but cannot replicate the dramatic restoration achieved by a hair transplant.
2. Is a hair transplant painful?
Hair transplant procedures are performed under local anesthesia. Patients may experience mild discomfort or swelling afterward, but modern techniques minimize pain.
3. How long does it take to see results?
Hair transplant results usually become visible after 3–6 months, with full results around 9–12 months. Non-surgical treatments may take several months of consistent use to show improvement.
4. Are there risks associated with hair transplants?
Minor risks include infection, scarring, or graft failure. Choosing an experienced surgeon and following post-operative care instructions reduces complications.
5. Can women undergo hair transplants?
Yes, hair transplants are suitable for both men and women, though the approach may vary depending on hair loss patterns.
6. Do non-surgical treatments work for all types of hair loss?
They are most effective for early-stage hair thinning or androgenetic alopecia. Severe or advanced hair loss may require surgical intervention.
Conclusion
Both hair transplants and non-surgical hair loss treatments offer valuable solutions depending on the stage of hair loss, desired outcome, and patient preference. Hair transplants provide permanent, natural-looking results for moderate to severe hair loss, while non-surgical options are convenient, non-invasive, and effective for early-stage thinning. By understanding the advantages and limitations of each approach, individuals can make informed decisions and create a personalized hair restoration plan that best suits their needs. Combining both strategies may also optimize results, ensuring a fuller, healthier head of hair over the long term.










